1. Gallbladder Disease :
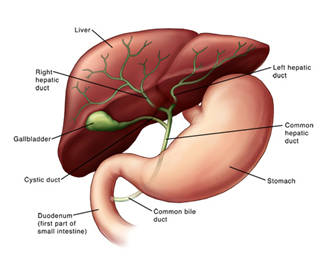
The term gallbladder disease is used for several types of conditions that can affect your gallbladder.
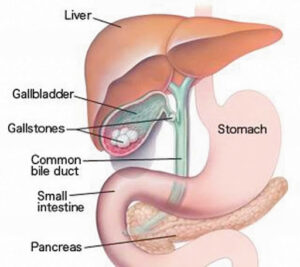
The gallbladder is a small pear-shaped sac located underneath your liver. Your gallbladder’s main function is to store the bile produced by your liver and pass it along through a duct that empties into the small intestine. Bile helps you digest fats in your small intestine.
Inflammation causes the majority of gallbladder diseases due to irritation of the gallbladder walls, which is known as cholecystitis. This inflammation is often due to gallstones blocking the ducts leading to the small intestine and causing bile to build up. It may eventually lead to necrosis (tissue destruction) or gangrene.
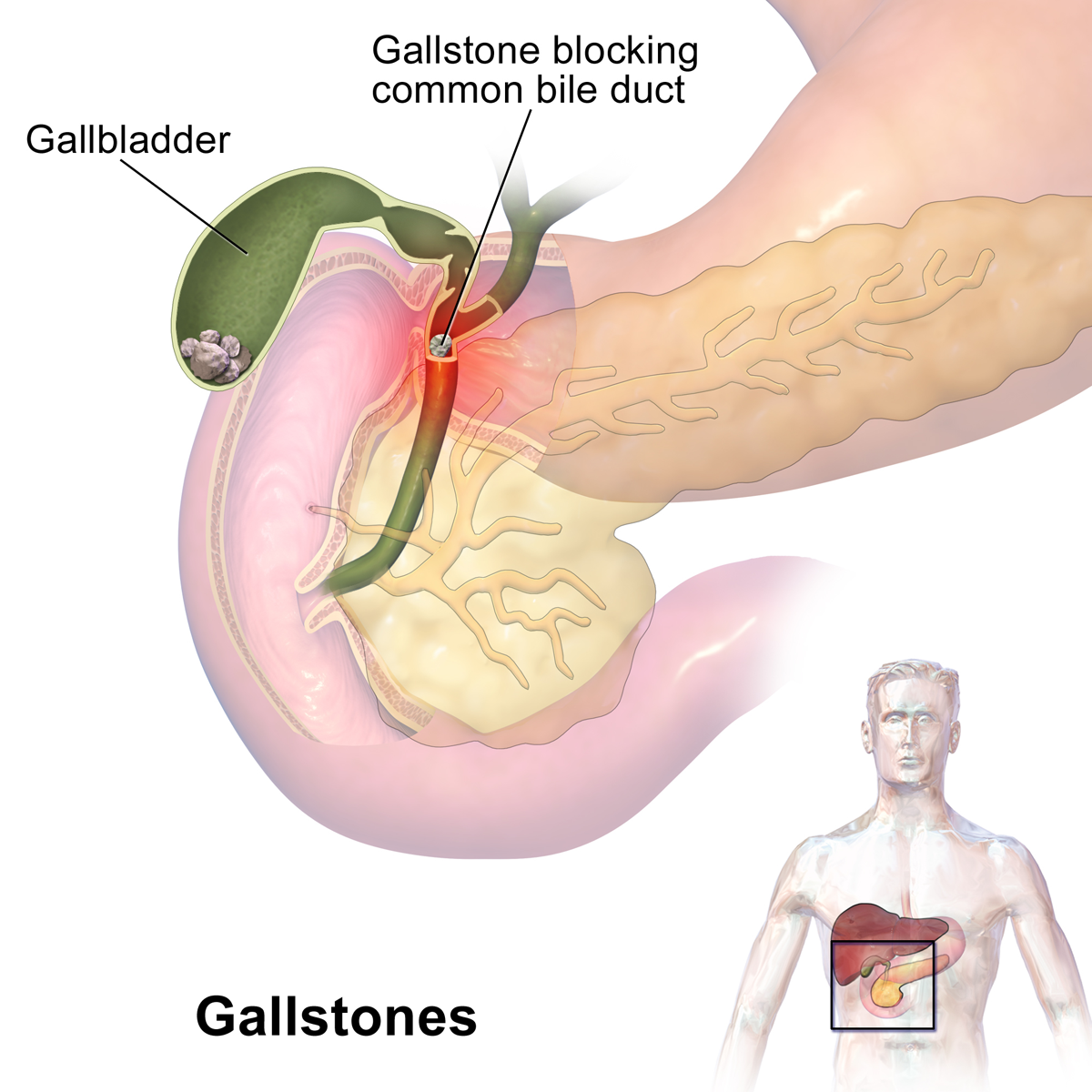
2. Gall bladder stones :
Gallstones develop when substances in the bile (such as cholesterol, bile salts, and calcium) or substances from the blood (like bilirubin) form hard particles that block the passageways to the gallbladder and bile ducts.
Gallstones also tend to form when the gallbladder doesn’t empty completely or often enough. They can be as small as a grain of sand or as large as a golf ball.
Numerous factors contribute to your risk of gallstones. These include:
- being overweight or obese
- having diabetes
- being age 60 or older
- taking medications that contain estrogen
- having a family history of gallstones
- being female
- having Crohn’s disease and other conditions that affect how nutrients are absorbed
- having cirrhosis or other liver diseases
3. Cholecystitis :
Cholecystitis is the most common type of gallbladder disease. It presents itself as either an acute or chronic inflammation of the gallbladder.
Acute cholecystitis
Acute cholecystitis is generally caused by gallstones. But it may also be the result of tumors or various other illnesses.
It may present with pain in the upper right side or upper middle part of the abdomen. The pain tends to occur right after a meal and ranges from sharp pangs to dull aches that can radiate to your right shoulder. Acute cholecystitis can also cause:
- fever
- nausea
- vomiting
- jaundice
Chronic cholecystitis
After several attacks of acute cholecystitis, the gallbladder can shrink and lose its ability to store and release bile. Abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting may occur. Surgery is often the needed treatment for chronic cholecystitis.
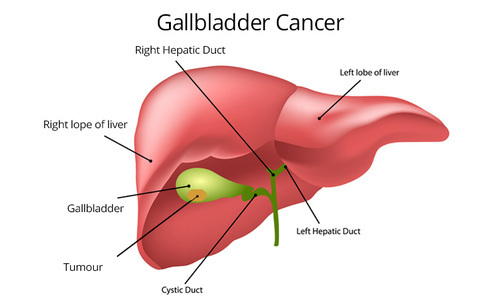
4. Gall bladder cancers :
Cancer of the gallbladder is a relatively rare disease. There are different types of gallbladder cancers. They can be difficult to treat because they’re not often diagnosed until late in the disease’s progression. Gallstones are a common risk factor for gallbladder cancer.
Gallbladder cancer can spread from the inner walls of the gallbladder to the outer layers and then on to the liver, lymph nodes, and other organs. The symptoms of gallbladder cancer may be similar to those of acute cholecystitis, but there may also be no symptoms at all.