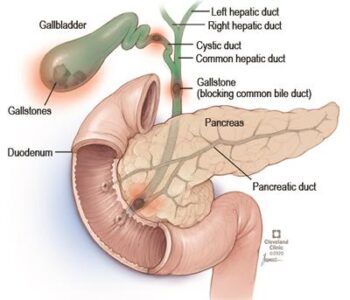
Cholecystitis is an inflammation of the gallbladder. Your gallbladder is a small pear-shaped organ tucked away under your liver in the upper right section of your abdomen. The gallbladder’s job is to store bile – a fat-digesting fluid made by the liver – and to release it after you eat a meal. Cholecystitis usually develops when the bile gets trapped in your gallbladder, and becomes infected with bacteria. Bile gets trapped when gallstones block the flow of bile out of your gallbladder.
Causes
- Cholecystitis occurs when your gallbladder becomes inflamed. Gallbladder inflammation can be caused by:
- Most often, cholecystitis is the result of hard particles that develop in your gallbladder (gallstones). Gallstones can block the tube (cystic duct) through which bile flows when it leaves the gallbladder. Bile builds up, causing inflammation.
- A tumor may prevent bile from draining out of your gallbladder properly, causing bile buildup that can lead to cholecystitis.
- Bile duct blockage.Kinking or scarring of the bile ducts can cause blockages that lead to cholecystitis.
- AIDS and certain viral infections can trigger gallbladder inflammation.
- Blood vessel problems.A very severe illness can damage blood vessels and decrease blood flow to the gallbladder, leading to cholecystitis.
Symptoms
- Signs and symptoms of cholecystitis may include:
- Severe pain in your upper right or center abdomen
- Pain that spreads to your right shoulder or back
- Tenderness over your abdomen when it’s touched
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Fever
Cholecystitis signs and symptoms often occur after a meal, particularly a large or fatty one.