Liver treatment depends on what kind of disease the patient is going through, Dr. Aniruddha Bhosale and his team provide Liver Disease Treatment in Pune and all kinds of preventive measures to keep your liver fit, even if your liver is completely healthy or fight against any liver disease.
1. Fatty liver :
Fatty liver is also known as hepatic steatosis. It happens when fat builds up in the liver. Having small amounts of fat in your liver is normal, but too much can become a health problem. Too much fat in your liver can cause liver inflammation, which can damage your liver and create scarring. In severe cases, this scarring can lead to liver failure.
2. Non-alcoholic steato-hepatitis :
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is an advanced form of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). NAFLD is caused by a buildup of fat in the liver. When this buildup causes inflammation and damage, it is known as NASH, which can lead to scarring of the liver. Scarring of the liver is a potentially life-threatening condition called cirrhosis.
Symptoms :
There are often no outward signs or symptoms associated with NASH. The most common symptoms are:
- Fatigue
- Pain in the upper right abdomen (usually mild)
NASH may lead to cirrhosis of the liver, causing one or more of the following symptoms as the condition progresses:
- Bleeding easily
- Bruising easily
- Itchy skin
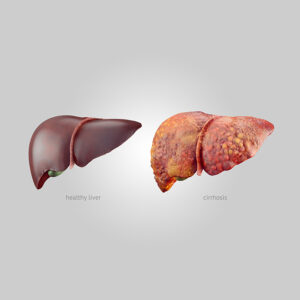
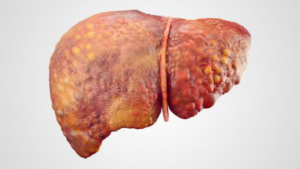
3. Liver cirrhosis :
- Cirrhosis is a complication of liver disease that involves loss of liver cells and irreversible scarring of the liver.
- Alcohol and viral hepatitis B and C are common causes of cirrhosis, although there are many other causes.
- Cirrhosis can cause weakness, loss of appetite, easy bruising, yellowing of the skin (jaundice), itching, and fatigue.
- Diagnosis of cirrhosis can be suggested by history, physical examination, and blood tests, and can be confirmed by liver biopsy.
4. Liver failure :
Liver failure is a life-threatening condition that demands urgent medical care. Most often, liver failure happens gradually, over many years. It’s the final stage of many liver diseases. But a rarer condition known as acute liver failure happens rapidly (in as little as 48 hours) and can be difficult to detect at first.
Liver failure happens when large parts of the liver become damaged beyond repair and the liver can’t work anymore.
There are two types of live failure:
- Acute: This is when your liver stops working within a matter of days or weeks. Most people who get this don’t have any type of liver disease or problem before this event.
- Chronic: Damage to your liver builds up over time and causes it to stop working.
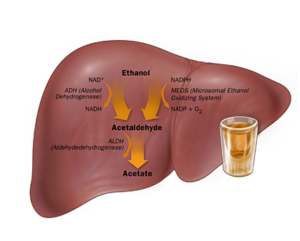
5. Alcoholic liver disease :
Alcoholic liver disease is a result of overconsuming alcohol that damages the liver, leading to a buildup of fats, inflammation, and scarring. It can be fatal.
The condition is a primary cause of chronic liver disease in Western nations.
The liver is one of the most complex organs in the human body, with over 500 functions. These include filtering out blood toxins, storing energy, making hormones and proteins, and regulating cholesterol and blood sugar.
Liver damage can affect the whole body. Once damage begins, it can take a long time to become noticeable, as the liver is generally highly effective at regenerating and repairing itself. Often, by the time the damage is found, it is irreversible.
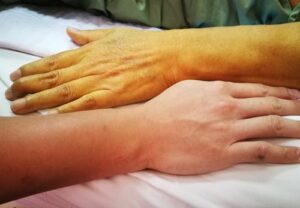
6. Jaundice :
It’s a disease that turns your skin and the whites of your eyes yellow. Newborn babies often get it. But adults can, too. See a doctor right away if you think you have jaundice. It could be a symptom of a liver, blood, or gallbladder problem.
Jaundice happens when there’s too much bilirubin, a yellow-orange substance, in your blood. It’s found in your red blood cells. When those cells die, the liver filters it from the bloodstream. But if something’s wrong and your liver can’t keep up, bilirubin builds up and can cause your skin to look yellow.
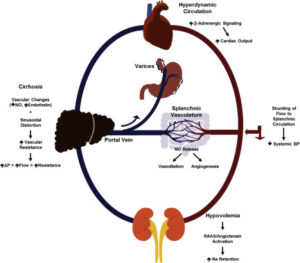
7. Portal hypertension :
Portal hypertension is an increase in the pressure within the portal vein (the vein that carries blood from the digestive organs to the liver). The increase in pressure is caused by a blockage in the blood flow through the liver.
Increased pressure in the portal vein causes large veins (varices) to develop across the esophagus and stomach to get around the blockage. The varices become fragile and can bleed easily.
8. Non-cirrhotic portal hypertension :
Non-cirrhotic portal hypertension (NCPH) includes a heterogeneous group of conditions. The aim of this paper is to make an overview on the denominations, diagnostical features and management of porto-sinusoidal vascular disease (PSVD) and chronic portal vein thrombosis (PVT) being the main causes of NCPH in the Western world.
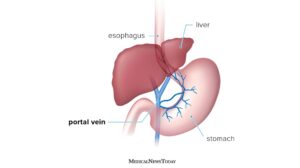
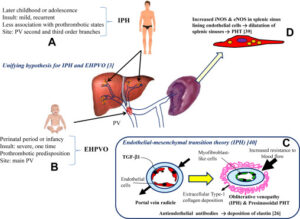
9. Extrahepatic portal vein obstruction :
Most people have no symptoms, but in some people, fluid accumulates in the abdomen, the spleen enlarges, and/or severe bleeding occurs in the esophagus.
Doppler ultrasonography can usually confirm the diagnosis. The cause is treated if possible, related problems are treated, and drugs may be used to dissolve the clot or to prevent the clot from enlarging or recurring.
10. Metabolic liver diseases :
The metabolic liver diseases, including Wilson’s disease, hereditary hemochromatosis, and α1-antitrypsin disease, are all indications for transplantation once the liver has irreversible damage. Because all these diseases have systemic effects, the pretransplant workup must include a coordinated systemic workup to allow for identification of systemic disease that would preclude transplantation. Hemochromatosis can lead to iron deposition in the myocardium and thereby result in irreversible cardiomyopathy or conduction system damage with arrhythmia. Cardiac dysfunction is a primary reason why mortality after transplantation is higher for hemochromatosis than for other indications. α1-Antitrypsin deficiency can lead to pulmonary emphysema, which requires careful cardiopulmonary evaluation to exclude pulmonary insufficiency or pulmonary hypertension.
11. Autoimmune liver diseases :
Autoimmune Hepatitis Symptoms
You might not notice any symptoms. If you do, they can range from mild or severe. Symptoms like fever, belly pain, and yellowing of your skin and eyes may come on suddenly. More often, the signs show up over weeks or months.The most common symptom is feeling tired. You may also have:
- Joint or muscle pain
- Lack of appetite and weight loss
- Nausea, vomiting, or belly pain
- Acne and skin rashes
12. Liver Trauma :
The liver is the most regularly injured organ in blunt abdominal trauma. Given its large size in the abdominal cavity, it can also be frequently injured with penetrating abdominal injuries. Liver trauma can run the gamut of minor lacerations or capsular hematomas with minimal morbidity and mortality to hepatic avulsions with high mortality. Most hepatic injuries are minor and can be graded with the American Association for the Surgery of Trauma Hepatic Injury Scale. Interventional radiological procedures can be used to treat traumatic hepatic injuries. This activity describes the causes of liver trauma, its presentation, diagnosis, and the role of the interprofessional team in its management.
13. Liver cancers :
Liver cancer is cancer that occurs in the liver. The liver is the largest glandular organ in the body and performs various critical functions to keep the body free of toxins and harmful substances.
The liver is located in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen, right below the ribs. It’s responsible for producing bile, which is a substance that helps you digest fats, vitamins, and other nutrients.
This vital organ also stores nutrients such as glucose, so that you remain nourished at times when you’re not eating. It also breaks down medications and toxins. When cancer develops in the liver, it destroys liver cells and interferes with the ability of the liver to function normally.
Liver cancer is generally classified as primary or secondary. Primary liver cancer begins in the cells of the liver. Secondary liver cancer develops when cancer cells from another organ spread to the liver.