1.GI Surgery :
Gastrointestinal (GI) surgery is a general term referring to procedures performed in the gastrointestinal tracts. When the digestive system is disrupted by disease, diet, or stress, GI surgery may be the best option.
What is it?
Gastrointestinal surgery is any surgery performed on an organ in the gastrointestinal tract. Contents that are subject to operation include the esophagus, mouth, stomach, and intestines.
What happens during the process?
Anesthesia is utilized during most GI surgeries. Once the patient is sedated under general anesthesia, surgeons will open the stomach. Next, the surgeon will work on repairing an organ within the digestive tract, from the esophagus to the lower intestine. During an anti-reflux esophageal surgery, doctors will take the upper section of the stomach and connect it to the lower part of the esophagus. During a gastrectomy, surgeons will remove either part of the stomach or the entire stomach and attach the esophagus to the lower intestine.
2.Liver resection surgery :
Liver resection is the surgical removal of a portion of the liver. This operation is usually done to remove various types of liver tumors that are located in the resected portion of the liver.
The goal of liver resection is to completely remove the tumor and the appropriate surrounding liver tissue without leaving any tumor behind.
What is the goal of liver resection?
The goal of liver resection is to completely remove the tumor and the appropriate surrounding liver tissue without leaving any tumor behind. This option is limited to patients with one or two small (3 cm or less) tumors and excellent liver function, ideally without associated cirrhosis.
As a result of these strict guidelines, in practice, very few patients with liver cancer can undergo liver resection. The biggest concern about resection is that following the operation, the patient can develop liver failure.
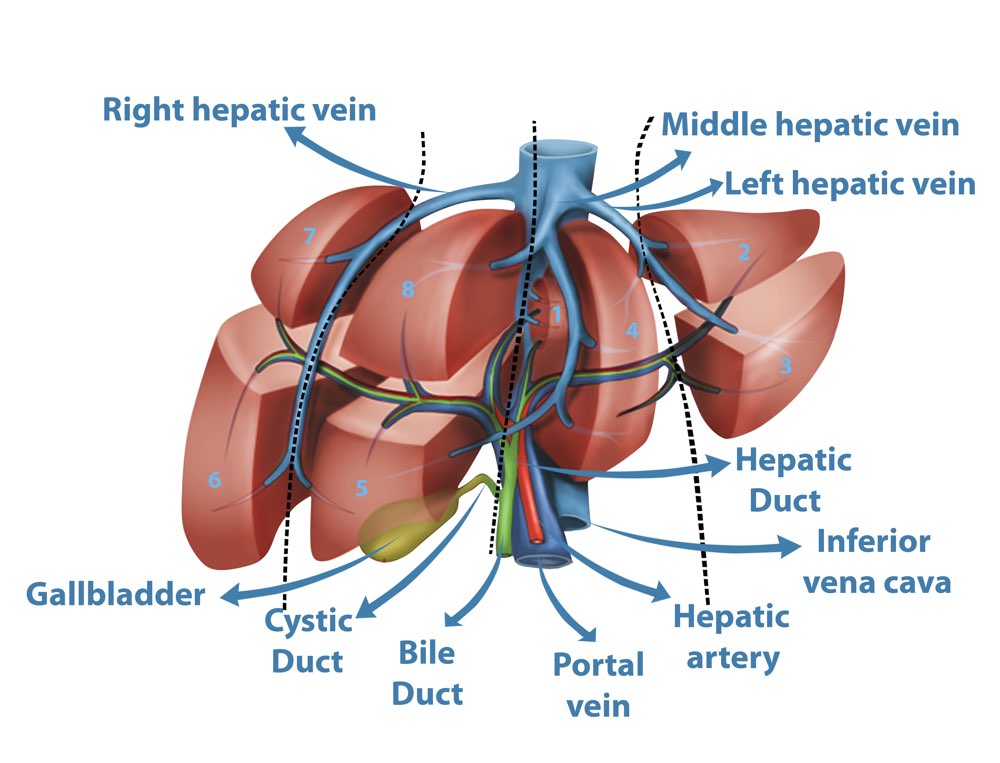
3. Bile duct surgery :
Common bile duct exploration is a procedure used to see if something like a stone is blocking the flow of bile from your liver and gallbladder to your intestine. The procedure is done under general anesthesia.
Bile duct exploration is a procedure that is performed to see if anything, such as a stone, is blocking the flow of bile from the liver and gallbladder to the intestine.
What are the risks of bile duct exploration?
As with any surgery, there are risks with bile duct exploration, including:
- Complications from general anesthesia.
- Swelling or scarring of the bile duct.
- Bile leak.
- Bleeding.
- Infection.
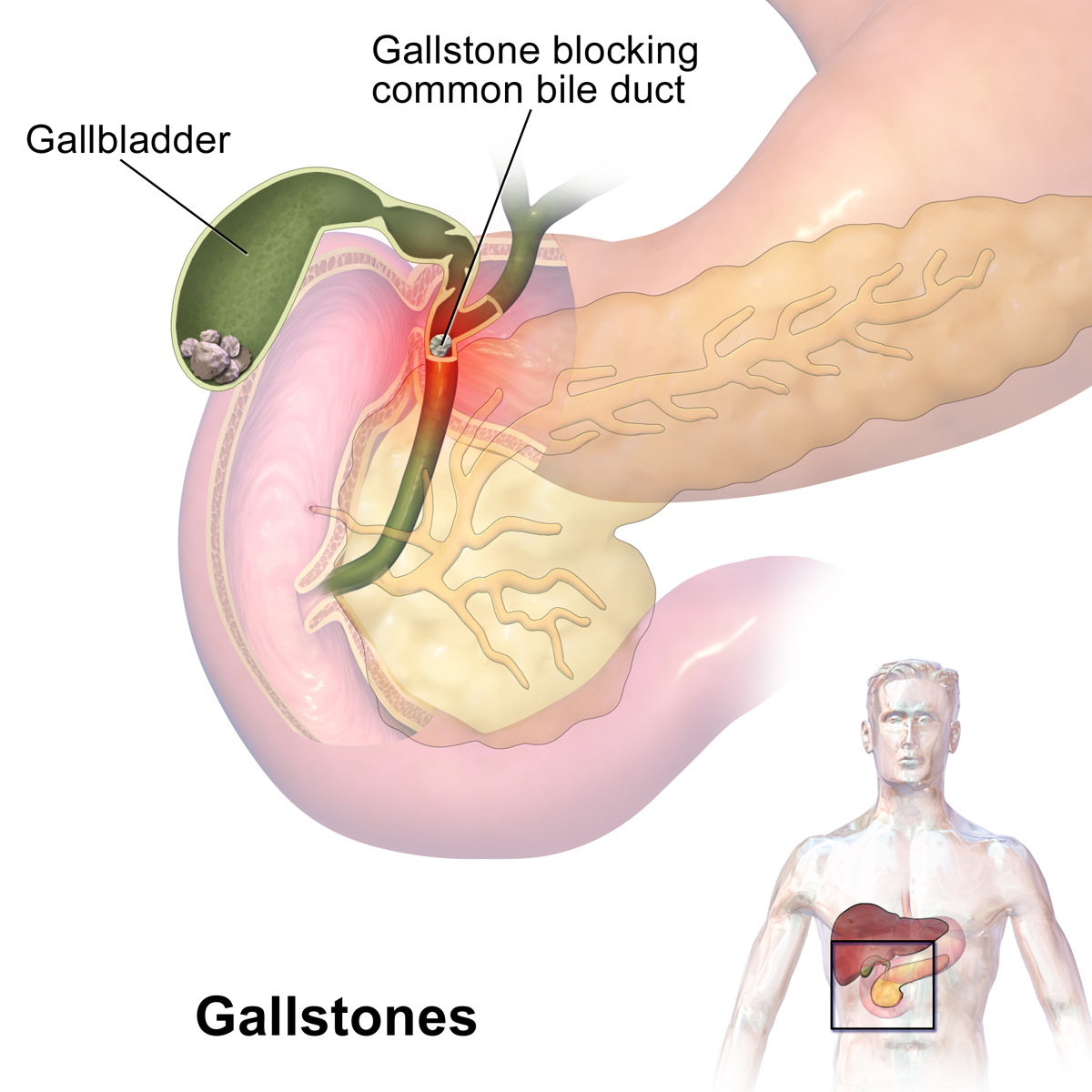
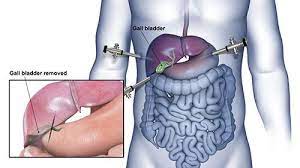
4. Gall bladder surgery :
The gallbladder is a small organ located on the underside of the liver. Its primary purpose is bile storage. The liver makes bile, a substance that helps the body break down and absorb fats. The gallbladder then stores the extra bile the liver makes. It releases bile when you eat a meal with fats that need to be digested.
Normal digestion is possible without a gallbladder. Bile will continue to reach your small intestine, but it just won’t be stored along the way in the gallbladder.
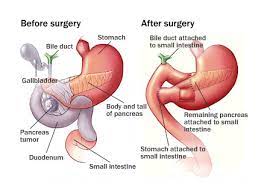
5.Pancreatic surgery :
For chronic pancreatitis, surgery may be recommended if chronic inflammation has caused a blockage in the pancreatic ducts. Surgery can help prevent further damage to the pancreas and alleviate symptoms like persistent pain.
Pancreatic surgeons at NYU Langone work as a team with imaging specialists using advanced diagnostic techniques to locate the areas of the pancreas where damage has occurred. For many people, surgery can be performed using minimally invasive, or laparoscopic, techniques, which require smaller incisions.